Explore the Shoemaker Protocol: A Pathway to Healing Mold Illness
This section presents an overview of the Shoemaker Protocol, outlining its 12-step treatment process for mold-related illness. It explains the diagnosis, lab testing, and the critical importance of following each step in sequence to achieve optimal recovery.
Understanding the Shoemaker Protocol
The protocol used in the treatment of mold illness is straight forward, but there are a series of steps to be taken, each in its proper order. The idea is that these treatment steps are similar to how one would climb a pyramid.
Ascending the pyramid step by step leaves a steadily smaller number of people with illness. There are different steps that address different abnormalities in the body. Until the patient has reached the final step, we don’t know that it’s final.
We always evaluate the actions taken so we don’t repeat labs unnecessarily. Any abnormal results of labs will be followed up with the next treatment step. At the end of the 12-step protocol, we make sure that all lab results have returned to normal.
The treatment protocol is simple to understand, yet strict adherence is required in the treatment sequence. Variations have been attempted and substitutions have been tried, and it has been substantiated; it is critically important to follow the pathway to health in the order it is prescribed.
The Diagnosis Process starts with an in-depth intake and differential diagnosis:
- There will be a complete patient history and identification of the symptoms being experienced, followed with lab tests. The labs needed to show inflammatory abnormalities are collected and the labs that are always normal in biotoxin illness are also collected.When the combination of history, physical exam, and VCS testing point overwhelmingly toward CIRS, treatment may be offered immediately. In cases which are less clear, the labs will confirm the diagnosis of CIRS or point in another direction.
A HERTSMI-2 building index test may be necessary to assure there is no continued exposure to the building with amplified fungal growth.
Then directives will be given to follow the order of treatment of the Shoemaker Protocol without being creative or substituting unproven or unsubstantiated ideas or methods in place of those proven to work.
Taking the Protocol Pyramid Step-by-Step
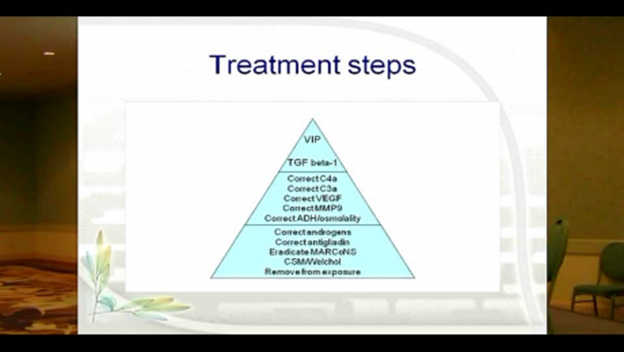
As we climb the pyramid, the next intervention is continually enacted that fixes each uncorrected item until the “top” of the treatment pyramid is reached. Each area is examined in a systematic order, supporting or ruling out, the most commonly affected areas.
The Steps of the Pyramid
Step One: the first level of the pyramid is removal from exposure.
This means no more working, schooling, or living in a moldy environment for CIRS-WDB illness patients. Exposure will need to be watched carefully.
If the root of the exposure issue is not found or addressed, or if there is another exposure situation, it can be likened to this bathtub analogy; when you’re trying to drain a tub filled to capacity with toxic substances, it’s going to be much more difficult, if not impossible, to fully drain it if you keep pouring in more of the same.
Step Two: the administration of Cholestyramine (CSM) or Welchol
The next step of the pyramid is prescribing the appropriate dose of cholestyramine, although most patients begin with Welchol these days for ease, convenience and reduced side effects.
These medications work to eliminate and correct toxin carriage in the body, and are administered with the necessary testing at regular intervals to determine effectiveness.
Step Three: eradicating biofilm-forming MARCoNS
If you find you still need to continue up the pyramid, the next step is the eradication of bacterial MARCoNS (Multiply Antibiotic Resistant Coagulase Negative Staphylococcus) from the nasopharynx, if present. These bacteria form a biofilm making it hard for many antibiotics to penetrate, sheltering the bacteria. Further, they are resistant to at least two classes of antibiotics. MARCoNS rarely exist if a patient has a normal MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone), but normal MSH is unusual in CIRS patients. To treat MARCoNS, a combination of therapies is used, including EDTA. The EDTA clears the way for normal nasal flora to eradicate the MARCoNS.
This is an evolving aspect of microbiology as MARCoNS rapidly acquire resistance, especially when drugs like the antifungals used in the past create resistance.
Step Four: eliminating gluten for those with anti-gliadin positivity as shown by a positive blood test.
The fourth step is correction of antigliadin antibodies. Many, but not most, patients will have a positive antigliadin antibody (AGA) in their initial lab work. When Celiac Disease is ruled out, treatment of patients consists of a gluten-free diet for three months followed by retesting. If the AGA is negative on retesting, gluten can often be reintroduced into the diet without consequences.
Step Five: correcting abnormal androgens
The fifth step is correction of abnormal androgens typically caused by an up-regulated aromatase enzyme. Treatment may consist of DHEA (dihydroepiandrosterone), HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) injections (or sublingually) for 5 weeks, or VIP (vasoactive intestinal polypeptide) nasal spray for 30 days.
Step Six: correcting ADH/osmolality
Step 6 is to correct antidiuretic hormone/osmolality problems. Treatment consists of desmopressin tablets every other night for 10 nights. If you have correction of this quickly, there is no need to continue but many people will need to have daily desmopressin for approximately one month. Osmolality needs to be closely watched.
Step Seven: correcting MMP-9, plus the “No Amylose Diet”
The seventh step is to correct MMP-9, an inflammatory marker. This treatment entails using omega 3 fatty acids, usually EPA and DHA, in conjunction with a “No Amylose” diet for the same time period.
The No-Amylose Diet was developed by Dr. Shoemaker to help people with mold illness who have high levels of MMP-9. Cutting back on amylose, a carbohydrate found in mainly in starchy foods that grow underground like potatoes, sweet potatoes, peanuts, carrots, plus cereal grains, works to lower MMP-9 levels.
For the Shoemaker Protocol recommended MMP-9 reference ranges, refer to the article on the Surviving Mold site. The reference ranges published through the labs (Quest and LabCorp) now offer a broader range, and we’ve seen significantly different ranges used around the world. The Shoemaker Protocol’s reference range is consistent with the worldwide peer-reviewed published literature and clinical trials’ findings on MMP-9 treatment for CIRS due to WDB exposure or “mold illness.”
Step Eight: correcting low VEGF, plus the “No Amylose Diet”
During this step we follow low VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor, a signaling protein that promotes the growth of new blood vessels). People won’t have symptomatic improvement if VEGF is below 31. Correcting low VEGF involves the no amylose diet and omega 3’s as before for MMP9 correction.
Step Nine: correcting elevated C3a
Step 9 is the correction of high C3a. High dose statins are used to clear elevated C3a. Co-administration of CoQ10, beginning 10 days before starting the high dose statins will help prevent CoQ10 deficiency secondary to decreased HMG-CoA reductase function.
Step Ten: next, check for elevated C4a
This split product of the MBL (mannose binding lectin) pathway of the complement system is a key marker of how severe a patient’s CIRS is. In the past we could use Procrit to correct C4a, but the FDA has put a black box on erythropoietin use. Because it’s not available, we move on to follow the rest of the protocol and VIP.
Step Eleven: reducing elevated TGFB1
Step 11 is the correction of TGFB1 (transforming growth factor beta 1), an innate immune cytokine which is also a key marker of illness severity. Reduction begins by treating with Losartan for 30 days in adults. Self-monitoring and low blood pressure should occur daily and with the start of symptoms such as orthostats. As with all other therapies, abnormal labs should be redrawn at the completion of therapy.
Step Twelve: using low VIP to restore immune balance and regulation
Step 12 is the pinnacle of the pyramid. By this time, most patients will already have become much better with reduction or resolution of at least 75% of their baseline symptoms. Some will require this last effort. The criteria for use of VIP includes a normal blood test for lipase; a negative culture for MARCoNS; a normal HERTSMI-2; and a normal VCS test.
Particularly, if VIP is used to correct multiple gray matter nuclear atrophy see the 2017 paper on VIP on the Surviving Mold site. This use of VIP brings the most hopeful changes to those with cognitive effects and mold exposure.
VIP is not appropriate for patients who still have significant exposures or MARCoNS. It won’t work. As such, a HERTSMI-2 (building index score), plus appropriate labs and testing will be run. These tests will document if the patient’s body has been relatively cleared of toxin, that there is no major exposure and, indirectly, that MSH is moving in the right direction. Passing these tests at this time demonstrates the effectiveness of the previous 11 steps.
With resolution of the symptoms, there will be a final check to verify stability off medications.
Through the whole process, as well as when the protocol is completed, exposure has to be carefully monitored. If there is a new Water-Damaged Building (WDB) exposure during the protocol, its typical to have to go back to the bottom of the pyramid and start over. Needless to say, taking steps to prevent water damage and subsequent mold exposure is imperative.
We urge you to review the Protocol Essays written by Shoemaker certified physicians. You can print them and use them as a reference.
Certified Shoemaker Provider
Dr. Ming began the Shoemaker Certification process in 2016 and completed it in 2017. This combination of written, oral, and essay-based evaluation ensures that Certified Providers possess the highest level of competency in applying the Shoemaker Protocol in clinical practice.
Certified Provider vs. Proficiency Partner
| Feature | Shoemaker Certified Provider | Proficiency Partner |
| Program Start Date | 2013 | Late 2018 |
| Training Format | Comprehensive, multi-stage program | Short course, originally in-person, now also online |
| Written Exam | 211-question handwritten exam with short-answer and “select all that apply” questions; personally graded with comments by Dr. Shoemaker | 171-question multiple-choice online exam, automatically graded |
| Oral Exam | ✓ Live oral examination with Dr. Shoemaker | ✗ Not required |
| Essays | ✓ Two essays personally reviewed and accepted by Dr. Shoemaker — topics: Evidence-Based Medicine (view here) and Steps of the Treatment Protocol (view here) | ✗ Not required |
| Direct Evaluation by Dr. Shoemaker | ✓ Yes | ✗ No |
| Credential Level | Highest level of competency in the Shoemaker Protocol | Basic proficiency designation |
